Long-term high blood sugar increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, retinopathy, neuropathy and other diseases.
In addition, high blood sugar may cause damage to blood vessels, increase the burden on the heart, and even cause serious consequences such as stroke.
High-sugar, high-fat, and high-calorie diets can easily lead to elevated blood sugar and increase the risk of diabetes and other metabolic diseases.
On the contrary, a low-sugar, low-fat, high-fiber diet can help control blood sugar and prevent the occurrence of diabetes and its complications.
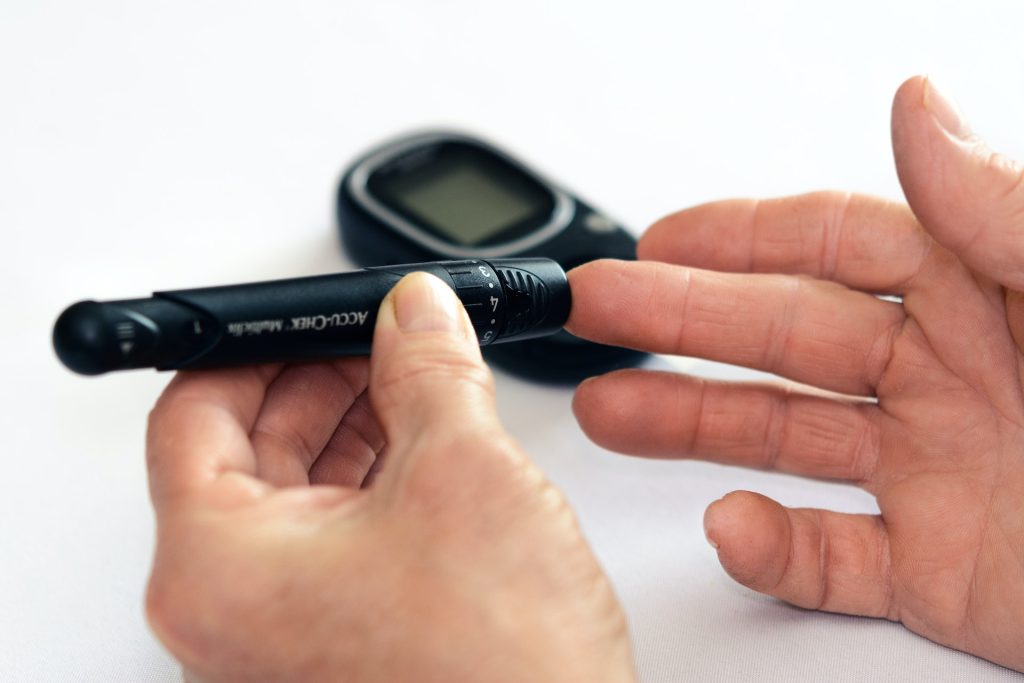
By regularly monitoring blood sugar levels, you can learn about blood sugar control in a timely manner and adjust your diet, exercise, and medication in a targeted manner to keep blood sugar within a stable range.
Continuous blood glucose monitoring helps prevent hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia, reduces the risk of diabetes complications, and improves quality of life.


High blood sugar can damage vascular endothelial cells and increase the risk of arteriosclerosis and cardiovascular disease.
People with diabetes are more likely to develop cardiovascular diseases such as high blood pressure and hyperlipidemia, and have a more difficult time recovering from a heart attack.
Long-term high blood sugar will inhibit the normal function of the immune system, reduce the body’s resistance to foreign invasions such as bacteria and viruses, and increase the risk of infection.
At the same time, high blood sugar can also affect the regulation of inflammatory responses, leading to an imbalance in inflammatory responses, which in turn affects the normal work of the immune system.
